Drivers Servo
Find dc motor and dc motor driver online? DFRobot.com provides Arduino DC Motor, Stepper Motor, Servo and motor drivers, electric muscle driver, shop now! All orders placed will be shipped out as usual, delivery times are expected to be affected due to COVID-19.Thank you for your continued support. Kinetix 5500 EtherNet/IP Servo Drives. Our Bulletin 2198 Kinetix® 5500 Servo Drives connect to and operate with CompactLogix™ 5370 controllers, supporting Integrated Motion on EtherNet/IP. With its innovative, compact design, the Kinetix 5500 drive helps minimize machine footprint and simplifies system wiring. Controllers & Drivers – AC Servo Drivers LE’s AC servo motors offer higher speeds and accelerations than DC types, as well as higher torques for larger actuators. Incremental and absolute pulse input drivers are available, as well as network models for CC-Link fieldbus protocol and Mitsubishi’s SSCNET.
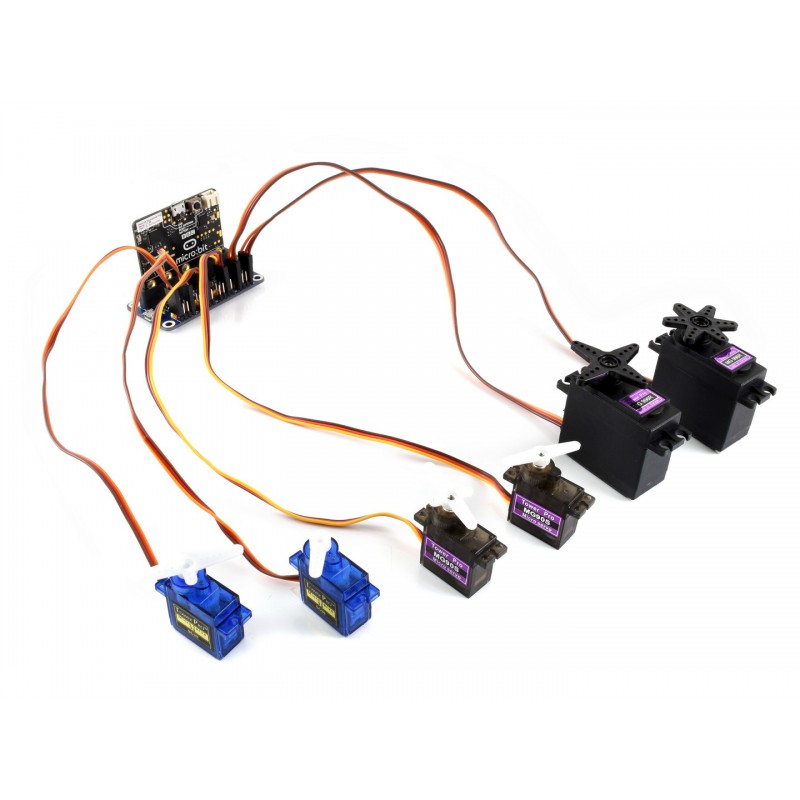
Introduction: WaveShare Motor/Servo Driver With Micro:bit
This Instructable will show you how to use a WaveShare motor/servo board with a micro:bit to power multiple servo motors. This board will make it possible to run more powerful servo motors than the micro servo motor that you can run directly from the micro:bit.
Technical information for the WaveShare board is here: https://www.waveshare.com/wiki/Motor_Driver_for_mi...

There is a similar board for driving up to 16 servos here: https://www.waveshare.com/servo-driver-for-micro-b...
Supplies:
- BBC Micro:bit
- WaveShare board: 'Driver Breakout for micro:bit', UPC: 614961953277
- power supply (battery pack or A/C adapter) - these must have JST connectors
- servo motor(s)
Step 1: Insert the Micro:bit
Insert the micro:bit into the long slot on the WaveShare board. The LEDs should be facing the outer edge of the board as shown above.
Step 2: Connect a Power Supply
Connect a power supply. This can be a battery pack or an A/C adapter. The power supply needs to have a JST connector. The first photo shows some options for power supplies.
Many power supplies have a barrel jack. You will need an adapter like the one shown above. It is called a Barrel Jack to 2-pin JST connector.
Your power supply should provide sufficient voltage to power your motor. The WaveShare board can take voltages up to 12V.
Drivers Services Department
Look for the brown 2-pin jack labeled GND/VCC and plug the power supply in there.
Step 3: Attach a Servo Motor
Look for the pins on the left side of the board in the area with black, red, and yellow pins. The pins are labeled 'GND', '5V', and 'S' at the top, and P0, P1, and P2 on the side.
Here, we'll plug a motor into pin 0 (P0). Match the wires on the servo to the colors on the board. These colors may vary, but ground is usually black or brown, power is usually red, and signal can be white or yellow.
Step 4: Use MakeCode to Program Your Servo
Now we need some code to have the micro:bit run the motor we have connected to the WaveShare board.

Open MakeCode and start a new project. (We are assuming that you have worked through the first few MakeCode tutorials). We are going to tell our servo motor to move back and forth 4 times when we press button A on the micro:bit. Drag the block 'On Button A pressed' from the 'Input menu'.
Next, add a loop. Drag a green 'repeat' block from the 'Loops' menu and snap it into the purple 'on button A pressed' block. So when we press button A, we're going to do something 4 times ...
Step 5: Send Instructions to the Servo Motor
We need to add some blocks to run our motor.
- Clicked on the 'Advanced' option at the bottom of the menu items.
- Select the item that says 'Pins'.
- Drag the red block that says 'servo write pin ... to ...' and snap it into the repeat block. Our servo is plugged into Pin 0 (P0), so select P0, and change the degree setting to 0.
- Add a light blue 'pause' block (found in the Basic menu) and change it to 500 ms (milliseconds).
- Then add another red servo block to move the servo to position 180 degrees,
- Add another pause block.
Looking at the complete code, it reads, 'when I press button A, do this 4 times: move the servo to position 0 degrees, wait 500 milliseconds, move the servo to position 180, wait 500 milliseconds.'
Click on Button A on the simulated micro:bit to see the servo move.
Step 6: Download the Code to Your Micro:bit
Plug the micro:bit into your computer using a USB cable. Click the download button, and drag the .hex file to the micro:bit.
[If you don't know how to do this, see the MakeCode quick guide.]
When you press button A on the micro:bit, your servo should run! Experiment by changing your code to use different settings for the servo positions, different numbers in the repeat loop, and different pause times.
Step 7: Run Something Cool With Your Servos!

We use our motors to run paper machines from our Paper Mechatronics projects. Check out the website to build your own machines and then hook them up to your servo motors. Have fun!
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. IIS-1735836. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
This project is a collaboration between The Concord Consortium, University of Colorado, Boulder, and Georgia Tech University.
Be the First to Share
Drivers Servomotores
Recommendations
Servo Drives
Ac Servo Drives
Microcontroller Contest
Automation Contest
Make it Glow Contest
